
Subscribe to continue reading
Subscribe to get access to the rest of this post and other subscriber-only content.


Subscribe to get access to the rest of this post and other subscriber-only content.
An herb as powerful as Mugwort is an invaluable way to connect and learn more about Goddesses of not only Greek, but Norse and Celtic mythology. Mugwort and its association with women, those who protect and champion women, as well as those seeking to expand their metaphysical world through dream and deity work, is as important today as it was thousands of years ago.
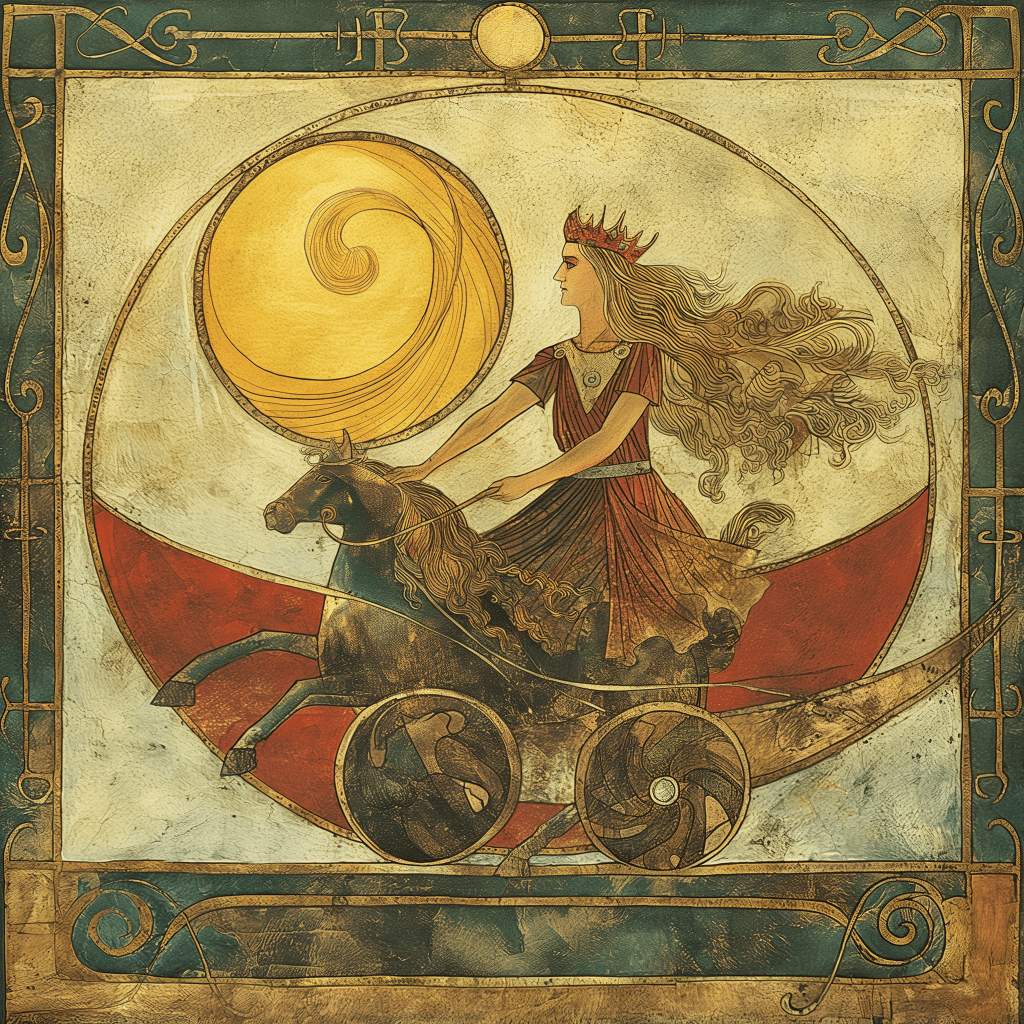
Artemis, the namesake of Mugwort, is the logical starting point. Artemis is a goddess of the hunt, the moon, and especially of female initiation and protection. She is associated with girls and women, but is also a goddess to boys and men in rites of initiation and the hunt. All who wish to learn more and work with her are welcome, as she is a goddess for everyone. Mugwort, having derived its name from her, is the mother herb mirroring her mothering prowess.
However, in the Greek mythos, she was not a goddess to suffer fools gladly. She vehemently defended her virginity and reputation as the greatest of hunters. Some sources suggest she was the patron goddess of the fearsome women warrior tribe, the Amazonians. A passionate and ferocious fighter for what she believes is right, a beacon for those who need strength.
Of everything that Artemis is known for, Mugwort is most closely related to her powers as midwife, a deity for both comforting women in labor and the newborn. Mugwort is also an important herb for dream and trance work, lending itself nicely to moon rituals, as Artemis was also a goddess of the moon. Using Mugwort in its tincture form, or burning as a smudge stick, will help to expand consciousness and enter a trance state for magical work. Adding Mugwort into your meditation on Artemis during the moon, especially the full moon, will greatly enhance communication.
In Norse mythology, Frigg, the most powerful volva, was believed to be the first practitioner of seidr magic. Frigg is the wife of Odin and a fiercely protective mother of Baldur. She is the goddess of family, motherhood, fertility and the balance of love and wisdom. Mugwort works perfectly with Frigg as it is an herb whose main use has been for assistance in prophetic dreaming and the overall health of women.
Runes that can be used when invoking Frigg are Fehu, Pertho and Berkano. Fehu, when related to Frigg, is a female rune for fertility concerned with livestock, and especially newly born cattle in spring. Fehu is always a rune of productivity. It can also be used for spiritual or artistic creativity, carrying a fiery power within. Fehu can also represent certain aspects of the life force.
Freya Aswin correlates Pertho with birth. Pertho can also be used to help find hidden aspects within yourself. The joining of these attributes with Frigg, who governs birth and is involved with weaving fate (through work as a volva and through seidr magic), very nicely encapsulates the magic of Mugwort.
The Berkano rune indicates birth, being rooted, and the feminine, has been called a rune of ‘bringing into being’, the first protection given to children at birth. Both Artemis and Frigg were known as unrelenting defenders of children and women. Incorporating Mugwort when working with Frigg can be very beneficial.
The goddess of Celtic mythology most closely associated with Mugwort is Brigid. Brigid is known as a goddess of fire, poetry, and healing; a maternal goddess who embodies the divine feminine. She is like spring, representing new beginnings.
As a goddess of fire and hearth, she was said to watch over all the fires in the homes of Ireland. She was closely associated with the sun and the warmth of spring, the time of renewal and rebirth. Mugwort is also an herb closely associated with fertility, the goddess, and of womanhood. Brigid, as a goddess that protected the flame (which was so important for ancient people’s survival), is like a mother radiating maternal compassion.
Poetry (and creativity) have always had close ties with the metaphysical and dream world, a world that Mugwort works so well in. Brigid was called upon to help with creativity and inspiration, especially with bards, who held a very high position in Celtic society. Bards were the keepers of history and culture, and Brigid was often invoked to help inspire creativity.
Brigid was also a goddess of healing. She was often called upon to help cure sickness and injury, as her touch was said to have healing powers. In addition to being a healer of sickness and injury, she was a goddess of childbirth, watching over women in labor. Her presence helped ease pain and ensured a safe delivery. She was also a protector of children and was asked by parents to watch over children’s safety and health. Brigid and her divine energies align well with Mugwort and its properties.

The Autumn Equinox is the turning point in the year when daylight and darkness are equal once again, tipping the scales towards the darkest period of the year when the nights grow longer and the weather gets colder. Traditionally, harvests would be reaped during this time and various rituals were conducted for the gods and spirits residing over abundance. Attention was given to the wights and ancestors, as it was believed that this time was liminal and that other realms were accessible. At the cusp of Equinox, the dark half of the year begins to slowly gain dominance.
Bonfires are especially common as well as sacrifices, whether physical or symbolic. People give thanks and ask for future harvests, ensuring a healthy stock of goods for the upcoming Winter months. Much depended on this pivotal time of year and many rites were undertaken to guarantee success. Feasts would be widespread as well as games, echoing other Summer and Fall festivals in atmosphere. For us here in the Northeastern United States, many crops are ripening during this time such as squash, corn, and apples. With this comes canning and drying goods to stock pantries for the Winter.
In “Teutonic Mythology” by Grimm, it says:
“In some parts of northern England, in Yorkshire, especially Hallamshire, popular customs show remnants of the worship of Frieg. In the neighborhood of Dent, at certain seasons of the year, especially autumn, the country folk hold a procession and perform old dances, one called the giant’s dance: the leading giant they name Woden, and his wife Frigga, the principal action of the play consisting in two swords being swung and clashed together about the neck of a boy without hurting him.”
As seen above, many early English (and Germanic) peoples would honor the god/goddess Frieg (Frigga) and Woden (Odin) during this time. Woden/Wotan in early Germanic belief was sometimes associated with wheat fields, where offerings were left for his horse Sleipnir during pivotal moments of the year. Certain epithets of Odin give reason to believe that he has been worshipped as a benevolent god to some extent, reigning over wealth, fate, and general prosperity. Names like this include Farmatýr (Lord of Cargoes) and Óski (God of Wishes).
Regarding Odin and continental Pagan belief, Grimm also states:
“As these names [Woden/Mercury/Hermes], denoting the wagon and the mountain of the old god, have survived chiefly in Lower Germany, where heathenism maintained itself longest; a remarkable custom of the people in Lower Saxony at harvest-time points the same way. It is usual to leave a clump of standing corn in afield to Woden for his horse.”
Of all the ancient celebrations, the Autumn Equinox was the most difficult one to find any references for. My belief is that it was a lesser celebratory event and more centralized in each community, where the harvest would be brought in and the local spirits offered to. People were likely working hard and didn’t have time to prepare for anything extravagant like they would during the last harvest of the year (Samhain), which certainly would have taken the forefront in terms of importance, at least to the Pagan Celts.
In “The One-Eyed God” by Kershaw, it says:
“These times of transition are strange times, whether the transition is from month to month, or season to season, or year to year; they are times which are not quite one thing or the other. They are like boundary lines, which are not quite my property or yours, or doorways, which are not quite inside or outside. As Eitrem said, it is at these dividing lines of time and space that the dead and Hermes are particularly active.”
It was common to not only focus on the harvest at this time, but to also give special attention to the dead and gods (or spirits) associated with death. The year was about to start its descent into darkness and the deified Sun/Light was to begin the darkest part of its journey through the underworld. Because of this, symbolic bonfires are lit to emulate the Sun and prolong the light.
In “Sorcery and Religion in Ancient Scandinavia” by Vikernes, it says:
“Odinn placed his eye in the grave, in the well of the past, every year, in order to learn from the past. This might sound strange, but his eye was the Sun, Baldr, that lost its power every autumn and therefore had to spend the winter in the world of the dead. In other words, Odinn had one eye in the world of the living and one eye in the world of the dead.”
Aside from the various gods, goddesses, and spirits of prosperity, it is clear that Odin and Frigga took a central role in (Germanic) Equinox observances in some areas of Pagan Europe. Odin (Woden) was recognized as a god of wishes, death, darkness, gifts, and clairvoyance, mirroring the exoteric liminality of the period between light and dark invoked by the Equinox. This external event is to also be reflected internally, as darkness begins to gain supremacy after this transition. We begin to look inward and conduct deeper spiritual work, creating light within to combat the impending darkness of Winter.

Harvest Moon hails!
This compilation includes 8 galdr tracks covering the first 8 runes of the Elder Futhark.
May practitioners find them useful.
Hailaz
“…To conclude, we see in these runes’ terrestrial concepts and duties; from establishing morals and ethics within society, to making sure there are enough physical resources available for all members of the tribe to prosper and carry on. We see images of farms, wagons, fertility gods, elements of the Germanic creation myth, the Earth, Sun, fire, and deep underlying rhythm that is the unseen law of life. Driving these runes are Raido and Gebo, representing the wheels and wagon, while Fehu and Uruz pull us forward; the cow and ox. Ansuz, Kenaz, and Wunjo represent the higher functions of mans existence; the arts, crafts, trades, spiritual practices, bliss, ecstasy and wisdom. Once the foundation of the tribe is laid in the form of resource security, the tribe can then thrive and push forward in the arts and spirit.”
-Wandering the Runic Path: Esoteric Analysis of the Germanic Runes
Ansuzsociety.com
#freyr #runes #galdr #paganism #harvestmoon
The Chanterelle is an edible mushroom with medicinal perks.
You can find this golden treasure living in symbiosis with pine, spruce, oak and hornbeam.
They will reappear in the same places year after year so long as the mycelium in the soil is not disturbed. One patch can produce fungi for generations.
Some of the benefits of Chanterelles include:
• Rich source of several vitamins and minerals including vitamin D which supports bone health
• Known to help reduce inflammation
• Great immunity boosters
We like to pickle our excess Chanterelles for later use.
Let us know if you have any favorite Chanterelle recipes or other uses!

The Summer Solstice is the time of year when the daylight is longest, the power of the Sun is at its peak, and the solar cycle reaches its apex, tipping the scales towards the dark half of the year once again. After this turning point, the sunlight begins to wane, shortening the daylight minute by minute until the Winter Solstice. Typically, this was a time to celebrate the Sun, spend time outdoors, and enjoy the bliss of good weather. Mead, wine, and other beverages would be consumed, and great feasts would be enjoyed.
In “Teutonic Mythology” by Grimm, it is said:
“Twice in the year the sun changes his course, in summer to sink, in winter to rise. These turning-points of the sun were celebrated with great pomp in ancient times, and our St. John’s or Midsummer fires are a relic of the summer festival. The higher North, the stronger must have been the impression produced by either solstice, for at the time of the summer one there reigns almost perpetual day, and at the winter one perpetual night.”
Games and various competitions would be hosted along with other festivities such as dancing and music. Entertainment would be lively and abundant, encouraging joy and merriment among the community. In the Germanic context, many people honor the god Baldr during this time as a god of light and/or personification of the light of the Sun, which in a mythological context, “dies” and beings to decline after this time, mirrored by Baldr’s death and descent into Hel. Because of these connections, a common blot/ritual focus during the Summer Solstice is the death (or funeral) of Baldr, the god of light. Stone ships are erected, abundant offerings are made, and various sacrificial items are thrown into fire. These offerings are meant to aid Baldr in his journey on the long road of the underworld.
In “Celtic Mythology and Religion” by Macbain, he says:
“The midsummer festival, christianised into St John’s Eve and Day, for the celebration of the summer solstice, is not especially Celtic, as it is a Teutonic, feast. The wheels of wood, wrapped round with straw, set on fire, and sent rolling from a hillock summit, to end their course in some river or water, which thus typified the descending course of the sun onward till next solstice, is represented on Celtic ground by the occasional use of a wheel for producing the tinegin, but more especially by the custom in some districts of rolling the Beltane bannocks from the hill summit down its side. Shaw remarks – “They made the Deas-sail [at Midsummer] about their fields of corn with burning torches of wood in their hands, to obtain a blessing on their corn. This I have often seen, more, indeed, in the Lowlands than in the Highlands. On Midsummer Eve, they kindle fires near their cornfields, and walk round them with burning torches.” In Cornwall last century they used to perambulate the villages carrying lighted torches, and in Ireland the Eve of Midsummer was honoured with bonfires round which they carried torches.”
Large bonfires and “Sun-wheels” are made during this time, reflecting the power and glory of the Sun. Special attention was given to the goddess during this time as well, whether as a deification of the Sun itself, the Earth, the Mother, or a mix of the 3. Offerings such as flowers, cakes, milk, honey, and blood are given to the gods and spirits, a ritual exchange of abundance for abundance. As observed in the above quote, it was (and is) common practice to bring the energy of the Sun down to Earth in the form of a torch, then parade it through the fields, groves, or temples in order to bless them with this powerful energy.
In “A History of Pagan Europe” by Jones & Pennick, it says:
“…But the summer solstice, under its statutory date of 25 June, became a popular festivity early in Germanic history. The German word Sonnenwende always refers, in medieval texts, to the summer solstice, not to the winter solstice. At the end of the first century CE some German troops in the Roman army at Chesterholme listed their supplies for the celebration in a record which has come down to us. In the early seventh century, Bishop Eligius of Noyon in Flanders criticised the chants, carols and leaping practised by his flock on 24.”
Here we are given examples of some ancient Germanic practices revolving around the Summer Solstice. We are told of singing, chanting, and competitive games like “leaping”. Clearly, the Christian Romans were disturbed by this revelry, showing its clear Pagan origins. This turning point in the year was extremely important to observe, as it strikes a pivotal moment in the Sun’s lifecycle, affecting every aspect of our lives.
The beginning of Spring is a magical time. Everything starts to wake up from Winter’s sleep, the air becomes perfumed by unfurling buds and shoots of green, birthed under sky and warming Sun. The birds start to unleash their full songs, filling the landscape with sound. In short, pure magic. What better time than now for one of the most magical plants to start its ascent skyward. Mugwort is now lining roads and walkways, growing unchecked in fields. I’ve taken the plunge into the world of Mugwort and would love to take you with me.
Mugwort (Artemisia Vulgaris) is one of the oldest herbs referenced in Anglo-Saxon plant wisdom. Some of its earliest known uses were to help regulate menstrual cycles, as well as with divination and dreamwork. There is also evidence of Mugwort smoke as an offering to Isis in Ancient Egypt. It has been mentioned in poems dating back as far as 3 B.C. in China, such as the the Shi King/Jing Poetry Classic. It is also mentioned in the poem “Hortulus” by Walafrid Strabo (808 AD – 849 AD), as ‘the Mother of Herbs’. Mugwort’s roots pre-date modern history.
The name Mugwort comes from the Greek Goddess Artemis, Lady of the Moon. She is the Goddess of hunting and fertility, also assisting in the cultivation of willpower and self-reliance. She is a comforter to women in labor, a helper to midwives, and protector of young girls. Mugwort is ruled by the planet Venus, lending it even more feminine energy. Hippocrates and Dioscorides even endorsed the use of Mugwort to help ease childbirth, their works having influenced modern medicine. The “Hippocratic Oath” that says “First do no harm” is from, well, Hippocrates.
The herb has many healing properties, both physical and spiritual. Physically, Mugwort may help stimulate menstruation, keeping from stagnation. It can be used for help in treating rashes, sore joints, bruises, and bug bites. Mugwort has benefits for pain relief, especially from arthritis. It has powerful nervine qualities, nervines being things that help relieve stress on your nervous system, which can be very helpful when treating anxiety, depression, and stress. Mugwort also contains things like iron, phosphorus, potassium, zinc, and tannin. It’s also a nutrient dense plant found most everywhere.
Personally, Mugwort is one of my favorite herbs. It has the ability to induce incredibly vivid dreams and the ability to bring about lucid dreaming experiences. Those are two of the main reasons why I love mugwort. Dream work is an important part of my spiritual practice, and Mugwort has been the best tool I’ve used. It can be taken as a tincture in tea, smoked, or put in dream sachets and bundles for burning. Being an herb so deeply entrenched in feminine energies, it is perfect for those that want to connect to the divine feminine, bond with their personal intuition, and enhance sensitivity. It can help open yourself to being more empathetic and patient.
Stagnation in body and mind can cause all sorts of problems. Mugwort increases circulation and warms the blood, helping a stagnating body. A stagnating mind will lead to frustration, detachment, and anxiety, just to name a few. Mugwort opens the mind, allowing for deep meditation and vision work. It can help with opening thoughts and deeper spiritual meanings. It moves the things in us which have lain dormant. It’s an herb for gentle but serious action.
Any phase of the Moon will work when using Mugwort for lunar practices, as it is a lunar herb. However, the best and most interesting time to use it would be during the Balsamic moon or when the moon is fully waned. The Balsamic moon is a time of going inward and recharging. This is the phase right before the new moon, making this moon perfect for meditation and really digging into the self. The Balsamic moon is the time to find what intentions you want to set and why you are trying to set that intention. Using Mugwort to explore your inner world will really help you bring your intentions to the surface; the perfect time to put your plans into action.

The Spring Equinox marks the traditional Easter celebration, the moment when the Sun crosses the equator from south to north. This is when animals like rabbits, deer, chipmunks, and other creatures of the forest begin to have their offspring. Various flora also emerge around this time, dotting the landscape with hints of color. During the Spring Equinox we pay special attention to the great Goddess in her youthful form of Ostara, Goddess of the Dawn. Ostara is associated with the rising Sun in the East, fertility, and light; a beacon of joy and good fortune. To many ancient Germanic Pagans, Ostara was credited with Springs deliverance. From her name we derive the modern word Easter, nodding to the Pagan origins of this holiday. To Ostara we make offerings and pray for a good year, thanking her for the return of the light. In one particular myth, Ostara transforms a bird into a rabbit who would then lay colorful eggs for her, showing us where the core symbolism of our modern holiday came from.
Hailaz Austra!
#ostara #spring #equinox #paganism

In honor of the season and the veil soon thinning, I have taken to studying more macabre and spooky plant lore for fun.
I hope that you enjoy this first tale.
Hungry grass, also known as Féar Gortach is said to be a patch of grass that is indistinguishable from any other section of grass. However, it is said to be cursed by the dead that lay buried underneath.
Should you stand or walk upon hungry grass, you will be overtaken by weakness and hunger.
Variations of the hungry grass story tell of a person stepping upon the grave or burial plot of a victim from An Gorta Mór (the Great Famine) of the 1840’s. The Irish term “féar gorta” can be more accurately translated as “famine grass” rather than “hungry grass.”
This myth may be a folklore manifestation of the historical trauma suffered during the Great Famine (An Gorta Mór) of the 1840’s. When the Famine took hold, men, women and children were left to starve to death as a direct result of the Potato Blight and a misuse of resources under British Government rule at the time.
Over one million people died in poverty, starvation and agony. These poor souls were thrown into mass graves, usually in fields. These spaces became known as “Famine Graveyards”.
The grass eventually grew over the buried bodies and it was said to be cursed.
When scientific reasoning wasn’t particularly widespread, it was probably a fair attempt at rationalizing the unexplained deaths or episodes of fainting that would occur from time to time due to malnutrition.
An alternative version of the hungry grass tale relates that anyone walking through it is struck by temporary hunger. In order to safely cross the grass, one must carry a bit of food to eat along the way such as a sandwich or crackers and some ale.
In a few rare accounts, the hungry grass is said to actually devour humans.
There was the idea that the hungry grass may also eat crops too. Before the term “hungry grass” was coined, people thought that a spirit of a man was, in fact, eating people. The word “féar” in Irish is both “man” and “grass”. So, Hungry Man came to be because they feared him. It was said that if you give relief to Hungry Man, you will enjoy unfailing prosperity, even during the worst periods of famine and death.
Although the hungry grass superstition is outdated nowadays and seems very specific to Ireland, it has a lot of narrative appeal.
Beware the hungry grass!

The scientific name for the common yarrow plant (Achillea millefolium) translates to ‘a thousand leaves’, in reference to the tiny, lacy, fern-like leaves. It is also called plumajillo (“little feather”) due to the shape and wispy characteristics of the leaves. Other names include chipmunk tail, milfoil, bloodwort, nosebleed plant, woundwort and field hops. The common name of yarrow may be derived from the Celtic word garw, which means “rough” and could be associated with yarrow’s ability to thrive in inhospitable conditions.
Yarrow was (scientifically) named after the Greek warrior Achilles, whose longevity in battle was credited to being dipped in a warm bath of yarrow shortly after birth. Later, it’s said that he used yarrow leaves to heal the wounds of his men. In keeping with this heroic legacy, yarrow is one of our strongest allies for heavy or hemorrhagic bleeding and first-aid herbalism.
Yarrow has long been associated with the occult and divination practice. It was considered an “herb of witches” due to its outstanding healing power. This could also have given rise to some of the common names for yarrow, such as bad man’s plaything, elf’s herb, devil’s plaything, devil’s herb and devil’s nettle. The Druids selected stems of yarrow to forecast weather for the season. The Irish included this as one of the herbs of St. John and hung it on houses as protection from sickness. In Celtic folklore, yarrow was used in handfasting and wedding rituals. It is said that yarrow keeps a newly married couple happy and at peace for seven years. I am not sure what happens after those seven years! Yarrow was also used by the Chinese as an oracle for foretelling the future.
Yarrow has been used in old European love charms for millennia. This plant is said to be a cure for heartache and has been used as a love charm. When the herb is pressed into a small sachet and placed under one’s pillow, it provokes dreams that can reveal the identity of one’s true love.
One Gaelic incantation that is recited when plucking yarrow goes like this: “I will pluck the smooth yarrow that my figure may be sweeter, that my lips may be warmer, that my voice may be gladder. May my voice be like a sunbeam, may my lips be like the juice of the strawberry…”
The Farmer’s Almanac published an article in 1986 that included an article titled “How to Find the Perfect Mate”. Several superstitious acts were listed, beginning with “Pluck a stalk of yarrow and stick it up your nose. If a drop of blood appears, your love is true.”
Yarrow was used by the Saxons as an amulet. These served as protection from all sorts of ailments and robbery. While it was used for security purposes, at the same time it could serve evil intents as well. Other legends state that when going on a journey, one should pull ten stalks of yarrow, keep nine, and throw the tenth away (as an offering to the spirits), place the nine under your right heel and evil spirits would have no power over you.
Amidst all the lore and practical uses, yarrow is also a ceremonial and mind-altering medicine. It is mildly psychotropic, and many herbalists have reported shifts in consciousness after taking high doses. When fermented in ale or mead, yarrow’s intoxicating effects seem to be enhanced. You won’t experience these effects if you’re taking yarrow in standard medicinal doses.
